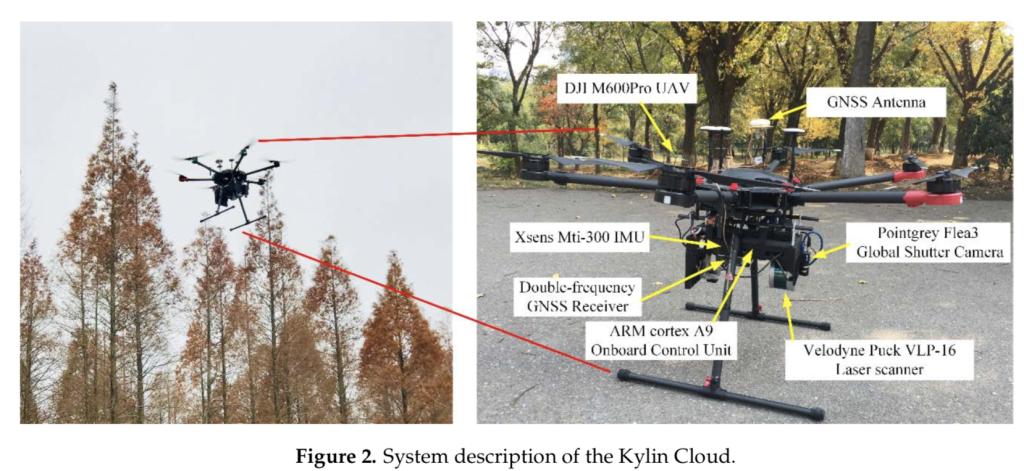
Jianping Li, Bisheng Yang*, Yangzi Cong, Lin Cao, Xiaoyao Fu,Zhen Dong, 2019. 3D Forest Mapping Using A Low-Cost UAV Laser Scanning System: Investigation and Comparison, Remote Sensing 11(6):717,DOI: 10.3390/rs11060717
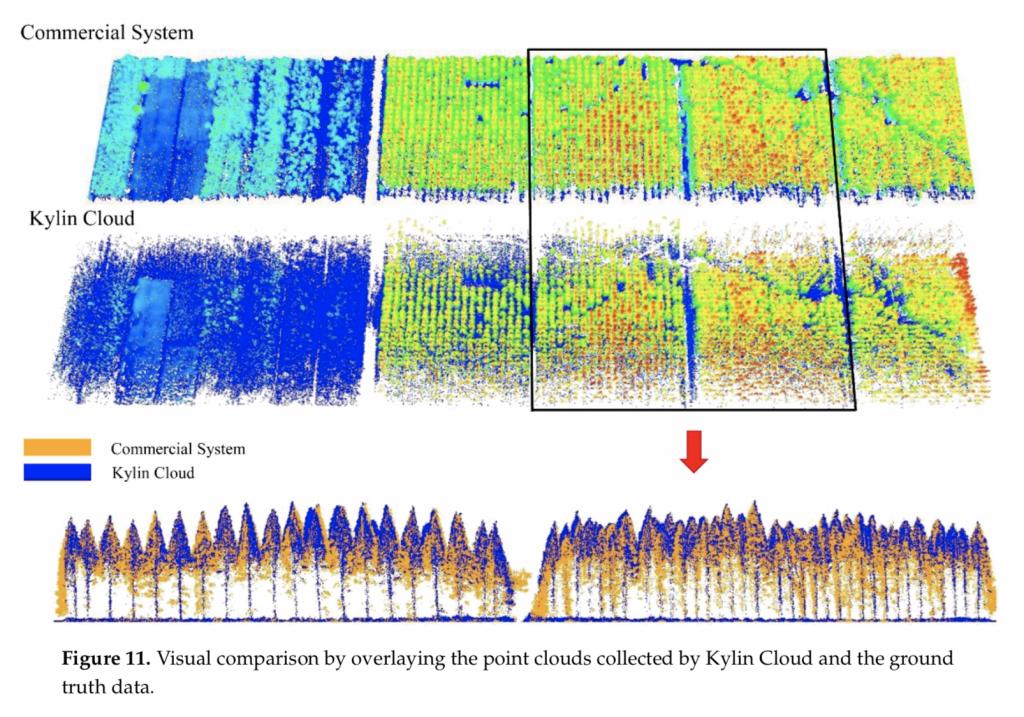
Abstract: Automatic 3D forest mapping and individual tree characteristics estimation are essential for forest management and ecosystem maintenance. The low-cost unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) laser scanning (ULS) is a newly developed tool for cost-effectively collecting 3D information and attempts to use it for 3D forest mapping have been made, due to its capability to provide 3D information with a lower cost and higher flexibility than the standard ULS and irborne laser scanning (ALS). As the direct georeferenced point clouds may suffer from distortion caused by the poor performance of a low-cost inertial measurement unit (IMU), and 3D forest mapping using low-cost ULS poses a great challenge. Therefore, this paper utilized global navigation satellite system (GNSS) and IMU aided Structure-from-Motion (SfM) for trajectory estimation, and, hence, overcomes the poor performance of low-cost IMUs. The accuracy of the low-cost ULS point clouds was compared with the groundtruth data collected by a commercial ULS system. Furthermore, the effectiveness of individual treessegmentation and tree characteristics estimation derived from the low-cost ULS point clouds were accessed. Experiments were undertaken in Dongtai forest farm, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province,China. The results showed that the low-cost ULS achieved good point clouds quality from visual inspection and compa rable individual tree segmentation results (P = 0.87, r = 0.84, F = 0.85) with the commercial system. Individual tree height estimation performed well (coefficient of determination(R 2 ) = 0.998, root-mean-square error (RMSE) = 0.323 m) using the low-cost ULS. As for individual tree crown diameter estimation, low-cost ULS achieved good results (R 2 = 0.806, RMSE = 0.195 m) after eliminating outliers. In general, such results illustrated the high potential of the low-cost ULS in 3D forest mapping, even though 3D forest mapping using the low-cost ULS requires further research.
Keywords: 3D forest mapping; low-cost; unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV); laser scanning



Download