标题:一种基于概率模型的文物碎片配准方法
A Probabilistic Method for Fractured Cultural Relics Automatic Reassembly
作者:Haiping Wang, Yufu Zang, Fuxun Liang, Zhen Dong, Hongchao Fan, Bisheng Yang
来源:ACM Journal on Computing and Cultural Heritage
摘要:
大量文物由于长期的埋藏和其脆弱性而破碎,配准修复后能在文化遗产研究中发挥更重要的作用。但是文物碎片配准存在例如断裂面特征少等诸多问题。本文提出了一种新型的断裂文物自动重装的概率方法,方法概述如下。
首先将配准流程概率化:
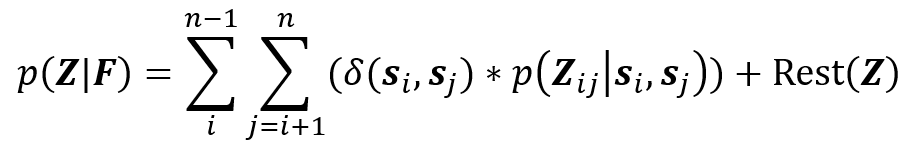
其中,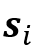 为提取的匹配单元,即分段断裂面,
为提取的匹配单元,即分段断裂面,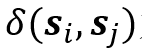 为匹配单元相似度,基于其空间分布预测任意两匹配单元间的刚性变换矩阵
为匹配单元相似度,基于其空间分布预测任意两匹配单元间的刚性变换矩阵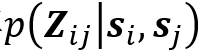 ,优化算法获取全局最优匹配策略,同时基于闭环检测,碰撞检测等构建冲突正则项Rest(Z)。
,优化算法获取全局最优匹配策略,同时基于闭环检测,碰撞检测等构建冲突正则项Rest(Z)。
实现流程如图1, 首先,通过二维描述子(LCD)和三维空间分布描述子(SDD)检测并描述一组匹配单元。其次,通过结合LCD和SDD描述符的相似性来进行匹配单元概率配对,并基于碰撞检测消除不正确的匹配对。最后,在闭环检测约束下,通过迭代优化得到全局最优匹配方案。


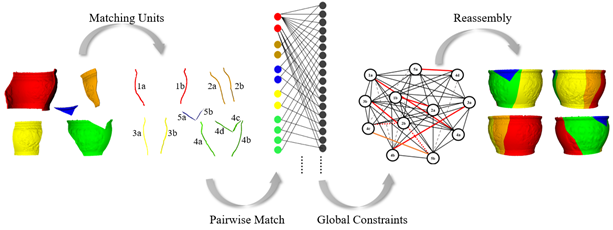
图1 配准流程
针对匹配单元的提取,如图2,通过种子点生长,基于空间相关性及指向一致性的融合,及离散点从重分配得到优化的分割匹配单元。
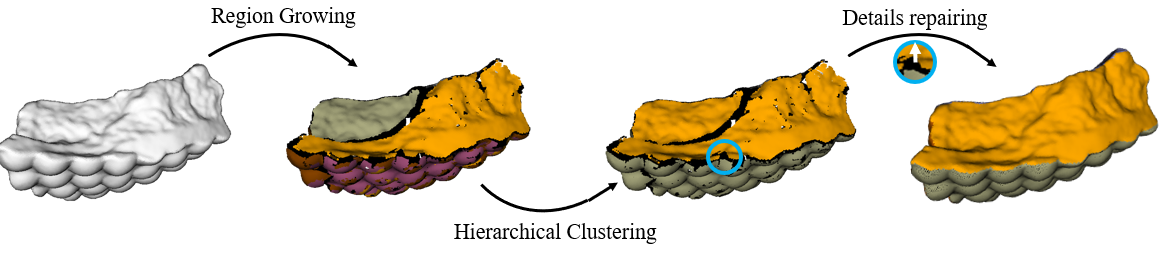
图2 匹配单元构建
随后,如图3基于最小损失投影及Douglas–Peucker算法获得匹配单元链描述子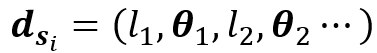 :
:
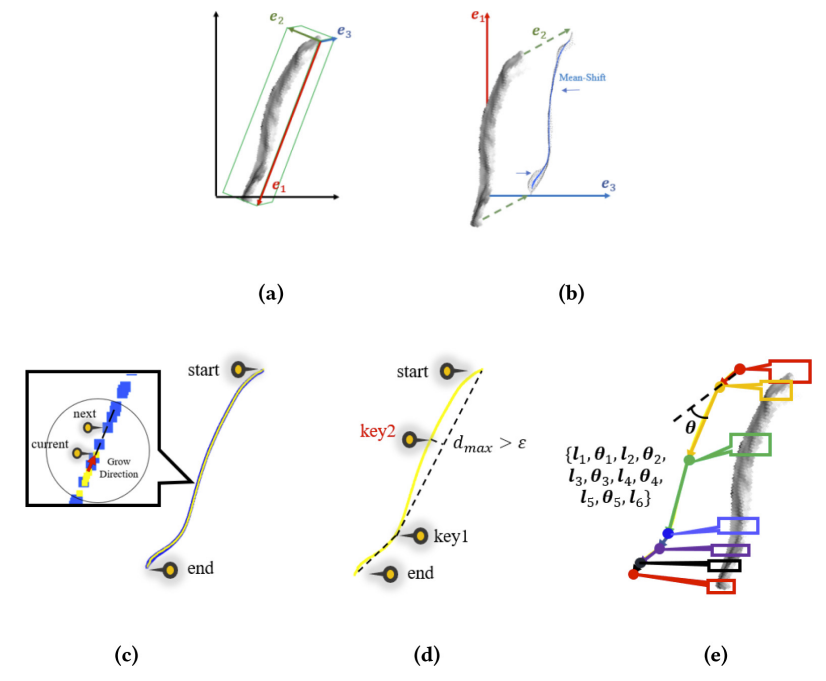
图3 描述子构建
基于此, 利用滑窗策略获取匹配子单元配对,并预测刚性变换矩阵,利用重叠度及碰撞检测获取矩阵可靠性概率:
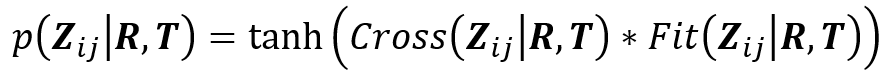
随后基于如图4重叠冲突检测及局部闭环检测进行匹配重分配。
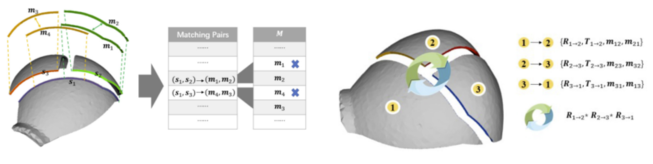
图4 重叠冲突及闭环检测
相关算法在模拟数据集及公开数据集上的匹配效果如图:


图5 匹配效果
Abstract:
Masses of fragile cultural relics are dug out in fragments due to long-standing burying and their fragility, which must be reassembled to play a role in cultural heritage study. However, it is very challenging to automatically reassemble a large collection of fragments of unknown geometric shapes. In this article, a novel probabilistic method for fractured cultural relics automatic reassembly is proposed to solve the problem in terms of good accuracy, efficiency, and robustness. First, a set of matching units are detected and described by the 2D Link-Chain Descriptors (LCD) and the 3D Spatial-Distribution Descriptors (SDD). Second, the pairwise reassembly probability is calculated by combining the similarities of LCD and SDD descriptors, then the collision detection is conducted to eliminate the incorrect overlapping pairs. Finally, a global optimal reassembly solution is obtained by iterative graph optimization with the constrains of the loop-closures and overlap restrictions. Comprehensive experiments with eight challenging datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieved good performance in terms of minor reassembly errors, efficiency and robustness to noise, varying point density and completeness.