标题:JoKDNet:用于大尺度室外TLS点云配准的联合关键点检测和特征表达网络
JoKDNet: A joint keypoint detection and description network for large-scale
outdoor TLS point clouds registration
作者:Yuan Wang, Bisheng Yang, Yiping Chen, Fuxun Liang, Zhen Dong
来源:International Journal of Applied Earth Observations and Geoinformation
摘要:
大尺度室外地面站(TLS)点云配准在很多对称及重复场景(如公园、森林和隧道等)仍然面临很多挑战,根源在于这些场景几何特征较弱,尤其是不同的时间段获取的数据(如山区)。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一个新的神经网络结构JoKDNet,同时学习关键点检测和特征表达,提高点云配准的精度和成功率。在没有使用ICP算法的条件下,实验结果表明JoKDNet在五种具有挑战性的场景(公园、森林、隧道、防空洞和山区)粗配准结果中,最大的旋转误差小于0.06°,最大的平移误差小于0.84m。
本文设计了同时进行关键点检测和特征表达的网络(图1),可以提取更鲁棒、更具区分性的关键点,同时提升特征表达能力,从而提升配准效果。
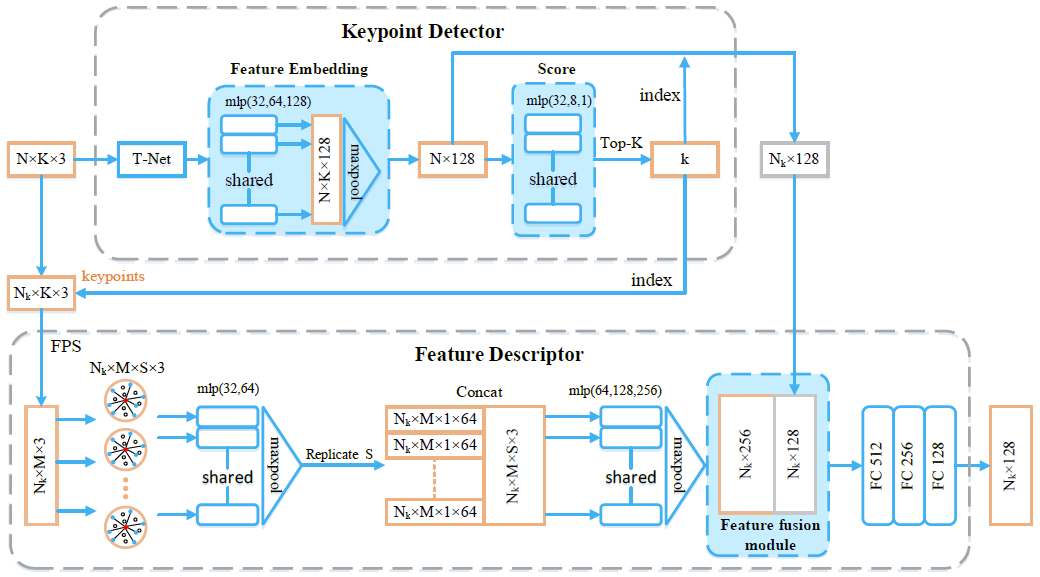
图1 关键点检测和特征表达模块
网络检测的关键点相比于传统的ISS方法大幅度提升了有效率(图2):
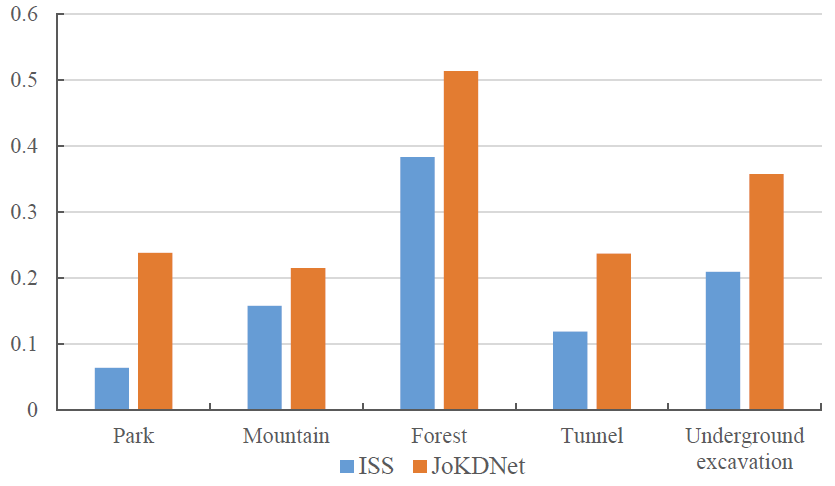
图2 ISS和JoKDNet检测的有效关键点对比图
使用JoKDNet网络对五种场景进行配准实验,结果如图3所示。相比于BSC,配准精度的均方根误差更小,证明JoKDNet更鲁棒;与GRPC方法相比,JoKDNet配准精度和成功率更高。
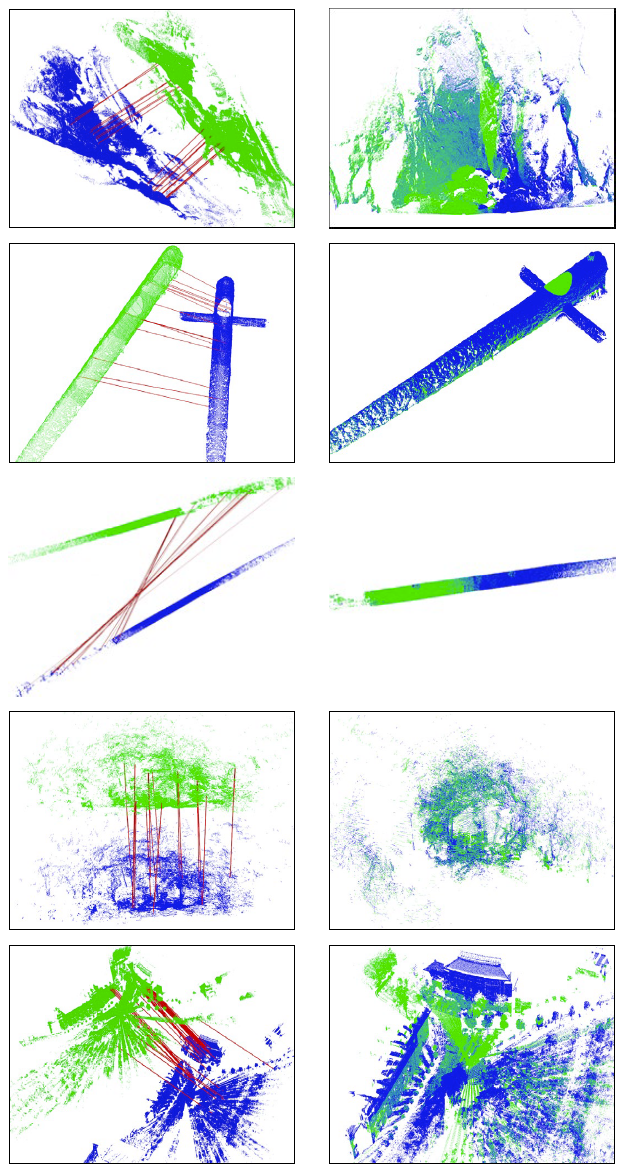
图3 五种场景的配准结果(左边为随机的对应点,右边为配准结果)
Abstract:
Registration of large-scale outdoor Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) point clouds remains many challenges in the scenarios with symmetric and repetitive elements (e.g., park, forest, and tunnel), the weak geometric features (e.g., underground excavation), and dramatically changes in different phases (e.g., mountain). To address these issues, a novel neural network JoKDNet is proposed to jointly learn the keypoint detection and feature description to improve the accuracy and feasibility of point clouds registration. Firstly, a novel keypoint detection module is introduced to automatically learn the score of each sampled point and regard the most significant Top-k sampled points as the detected keypoints. Secondly, an enhanced feature description module is proposed to learn the feature representation of each keypoint by fusing the hierarchical local features and context features. Thirdly, a loss function is designed to make the detected keypoints more distinguishable for matching, which simultaneously maximizes the feature distance between non-corresponding keypoints and minimizes the feature distance of corresponding keypoints. Finally, the distance matrix module and RANdom SAmple Consensus (RANSAC) are utilized to determine the correspondences of source and target point clouds for the transformation calculation. Comprehensive experiments show that the JoKDNet performs effectively on five challenging datasets (e.g., park, forest, tunnel, underground excavation, and mountain) in terms of registration errors, and robustness to varying scenarios, with the maximum rotation error less than 0.06° and maximum translation error less than 0.84m without ICP.