原文题目:Geometric Feature Enhanced Line Segment Extraction from Large-Scale Point Clouds with Hierarchical Topological Optimization
来源:International Journal of Applied Earth Observations and Geoinformation
作者:胡宗田,陈驰*,杨必胜,王治邺,马瑞琪,吴唯同,孙文鹿
背景:
三维激光扫描技术因其具有全天候、高速度、高精度、高密度等特点已经被广泛应用于新型基础测绘、双碳研究、无人驾驶、城市形态分析、地下空间探索等国家重大战略需求之中。三维激光点云的智能化处理也受到了国内外学者的深入研究,但目前大多数的研究都仅关注于某个特定的领域例如分割、配准等,或者只基于某个平台例如MLS进行数据处理。然而,我们可以从另一个角度即可以表达物理世界中通用对象的几何图元来理解点云。在点云中,基本单位是点坐标。由一组离散点组成的几何图元可以被视为点云在实体级别的一种抽象和表示。直线段作为最常见的图元,在点云处理的多个领域都作为一个重要且基础的基元,比如配准,三维目标检测,三维重建,SLAM 中的校正、定位等。但目前三维直线段提取的方法都存在着一定的问题,比如基于多视图的方法在3D-2D转化过程会造成边缘损失、基于点云局部特征的方法时很难计算出描述整个输入点云边缘的局部特征以及深度学习没有足够的训练样本等。本文针对从大规模点云中提取三维直线段所面临的科学问题,提出了一种基于几何特征增强和层次拓扑优化的直线段提取方法。
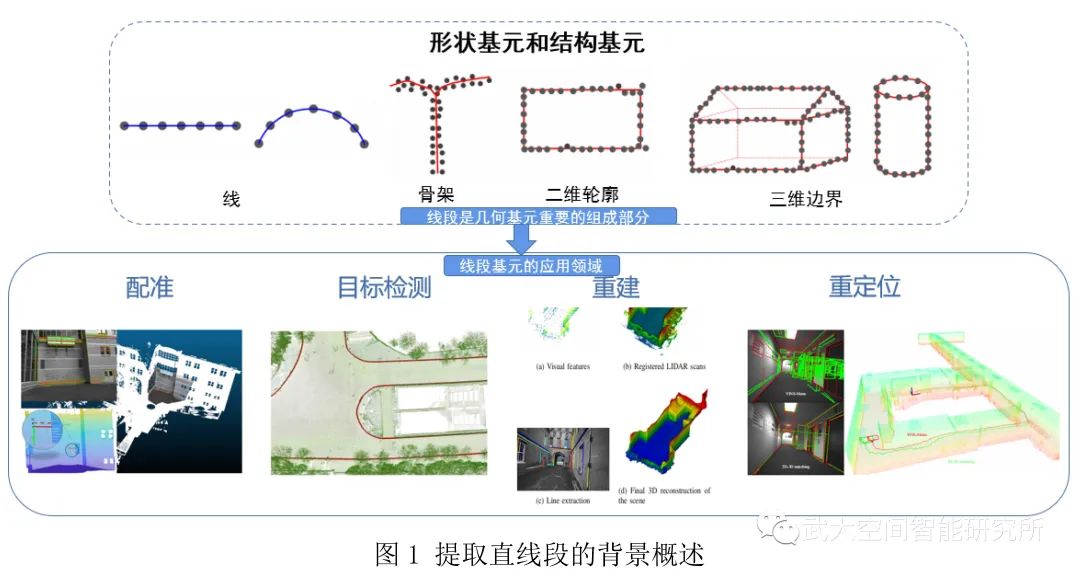
方法概述:
本文提出了一种基于几何特征增强和层次拓扑优化的大规模点云线段提取的方法,该方法主要以下三个步骤:
(1)投影平面区域提取。基于点云的局部几何特征进行区域增长和区域合并,从而提取了点云中的三维投影平面区域。(2)几何特征增强的三维直线段提取。将位于三维投影平面区域上的点投影到二维平面上,并将可以表征点云边缘的局部几何特性——最大特征向量周围的归一化一阶矩融合到投影图像的像素中,从而形成点云边缘特征增强的投影图像。然后基于DexiNed来定位投影图像的边缘,并利用MCMLSD算法从边缘中提取二维直线段,最后进行2D-3D反投影获得三维直线段。(3)三维直线段层次拓扑优化。对三维直线段进行层次拓扑优化,首先基于轮廓合并断线以恢复原始感知上准确的三维直线段,包括三维直线段的分组和合并;其次对合并后的线段集进行分层优化处理,包含基于轮廓地未封闭轮廓的封闭操作和基于线段地平面相交线的合并。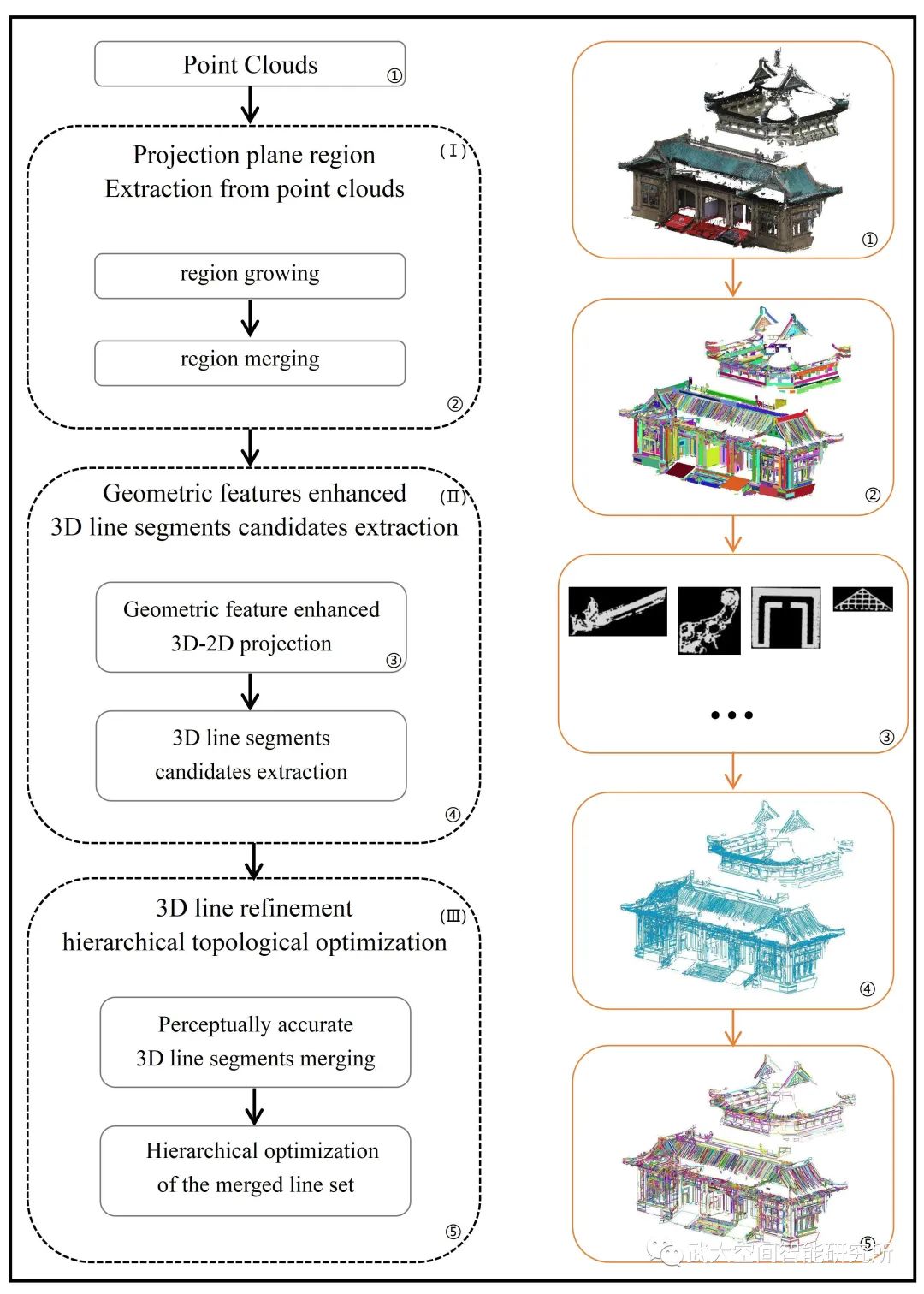
图2 文章中提取点云中直线段的流程图
实验结果:
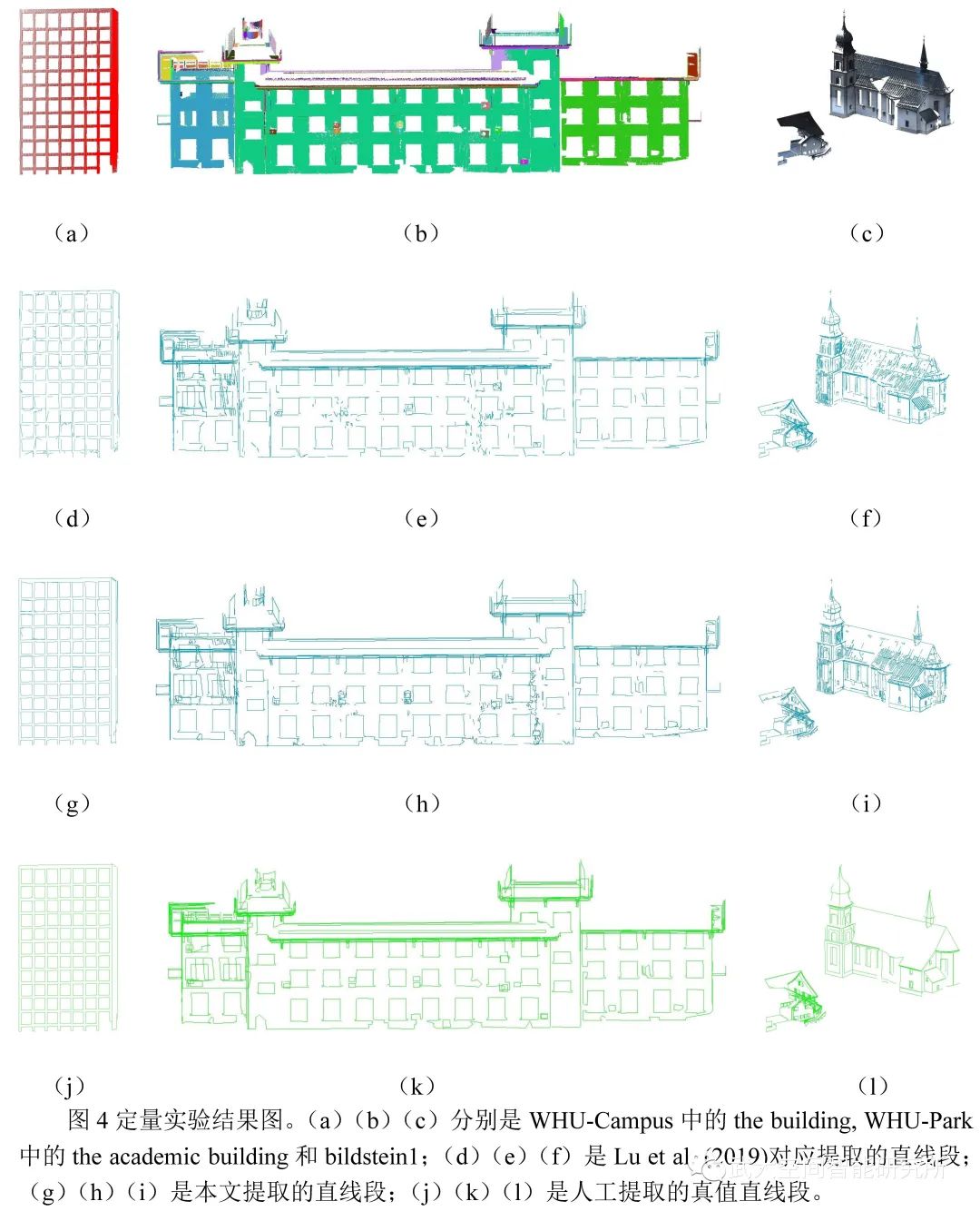
为了评估我们的算法,本文选取了几个有代表意义的自然和人工点云场景作为实验数据,这些数据主要来自于公开数据集Semantic3D和WHU-TLS(http://3s.whu.edu.cn/ybs/en/benchmark.htm),其中Semantic3D选择了的StSulpice、Bildstein1 和Buildstein3,WHU-TLS选择了Campus、Park 和Heritage building、Residence,实验结果如图3。图4展示了定量实验结果图,本文算法提取的Completeness和Correctness的平均值可以达到86%( dl, ds: 0.5,0.5)。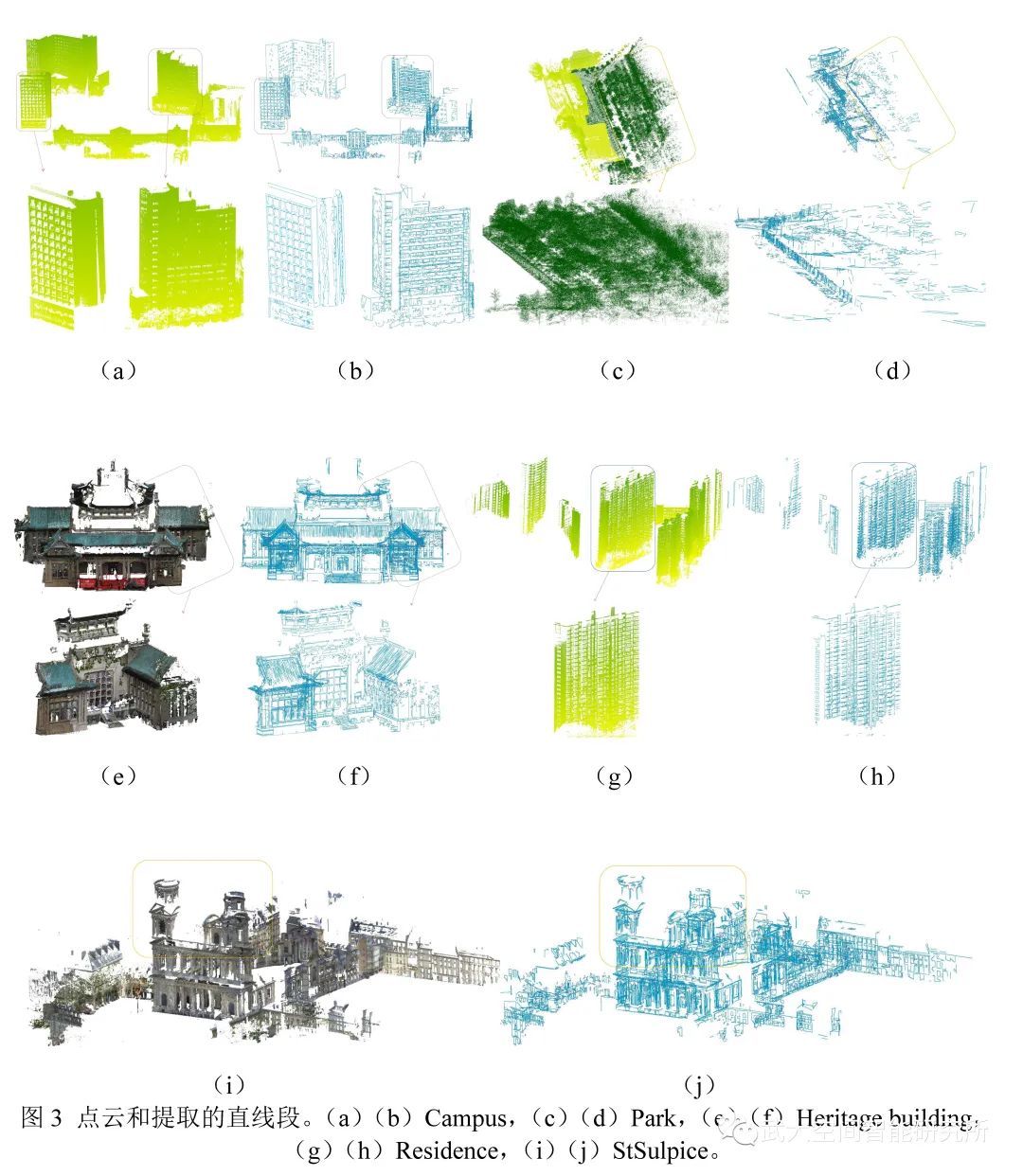
Abstract:
As the most common primitives, line segments play an essential role in the vectorized reconstruction of artificial scenes. In this paper, a geometric feature enhanced line extraction method with Hierarchical Topological Optimization is proposed to extract line segments from large-scale point clouds. Firstly, 3D projection plane regions are extracted from point clouds using region growing and merging; Secondly, the point clouds in the detected planar region are projected onto 2D grids for efficiently geometry features enhanced line detection. Specifically, the edge feature index of each point inside each projection grid is calculated and fused to represent the edge-geometry enhanced feature. The likelihood of edge presenting on the projection grids is produced using a pre-trained convolutional neural network that combines multi-scale edge locating outputs. Then, line segments on the projected edge maps are extracted by the MCMLSD algorithm and further back-projected into 3D space to form the 3D line segment candidates. Thirdly, the hierarchical topological relationships between the contour and line segments are used to optimize the candidate 3D line segments. The optimization process consists of merging perceptually accurate 3D line segments, closing the contour line based on the contour and merging plane intersection lines based on line segments. The point clouds of seven large-scale outdoor scenes from the Semantic 3D and WHU-TLS public datasets are selected for qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Experiments show that the proposed approach can efficiently extract line segments that represent the geometric characteristics of the scenes comprehensively and accurately. Compared with the SOTA line segments extraction algorithms (i.e., Lu et al. (2019), Zhang et al. (2020a)), the proposed method filters out major miscellaneous/broken lines and extract more complete line segments. The Completeness and Correctness of the line segments extraction results reach 86% on average compared with manual labeled ground truth (dl, ds: 0.5,0.5), at an average processing speed of 25,000 points per second.
图1和图4参考文献:
[1] Amblard, V., Osedach, T.P., Croux, A., Speck, A., Leonard, J., 2021. Lidar-Monocular Surface Reconstruction Using Line Segments. ArXiv preprint arXiv:.02761.
Lu, X., Liu, Y., Li, K., 2019. Fast 3D line segment detection from unorganized point cloud. ArXiv preprint arXiv:.02532.
[2] Mi, X., Yang, B., Dong, Z., Chen, C., Gu, J., 2021. Automated 3D Road Boundary
Extraction and Vectorization Using MLS Point Clouds. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp.
Syst. 23 (6), 5287–5297.
[3] Xia S, Chen D, Wang R, et al. 2020. Geometric Primitives in LiDAR Point Clouds: A Review[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 13: 685-707.
[4] Yu, H., Zhen, W., Yang, W., Scherer, S., 2020a. Line-Based 2-D-3-D Registration and
Camera Localization in Structured Environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 69
(11), 8962–8972.
[5] Yu, H., Zhen, W., Yang, W., Zhang, J., Scherer, S., 2020b. Monocular Camera
Localization in Prior LiDAR Maps with 2D-3D Line Correspondences. In: IEEE/RSJ
International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Electr Network,
pp. 4588-4594.