原文题目:DCPLD-Net: A diffusion coupled convolution neural network for real-time power transmission lines detection from UAV-Borne LiDAR data
作者:陈驰*,金昂,杨必胜,马瑞琪,孙上哲,王治邺,宗泽亮,张飞
来源:International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation
研究背景:
输电导线是输电设备的主要组成部分,在走廊内容易受到外力和环境侵蚀。几十年来,通过激光雷达数据或RoW检测获得的图像对输电线进行自动检测和诊断一直受到学术界和工业界的关注。目前,大部分输电线路的三维提取和分析都是基于激光雷达点云,且多使用基于规则的方法或传统的机器学习技术,这些方法在时效性和泛化性方面存在不足。为此,本文提出了一种将模拟物理扩散场与卷积神经网络相结合,从无人机激光雷达数据中实时提取输电线的方法。
研究方法:
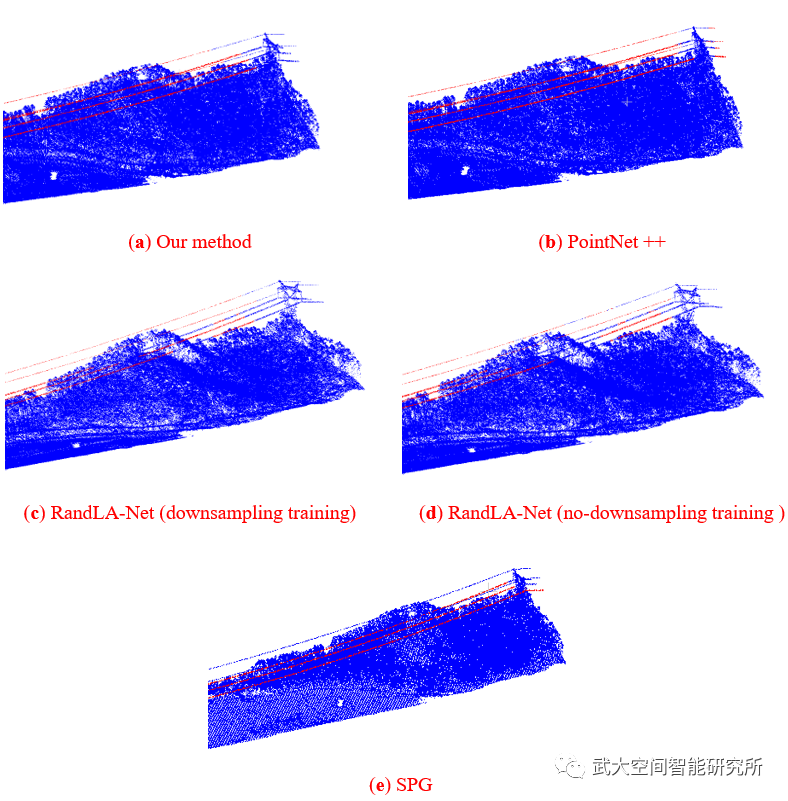
为了在三维点云上实现有效的二维卷积,我们提出了一种新的点云表示方法,称为横截面视图(Cross Section View, CSV),该方法将离散点云转换为由具有变形几何形状的体素沿飞行轨迹构造的三维张量。CSV特征生成后,将每个体素的编码特征视为能量(即热量)信号,在空间中进行扩散,生成扩散特征图。通过模拟物理过程(扩散),输电导线点的特征得到增强。最后,提出了一种名为PLDNet的单级检测器,用于扩散CSV表示上的输电导线的多尺度检测。
研究结果:
实验结果表明,在8 Hz的检测速度下,DCPLD-Net的F1得分达到97.14%。此外,在电力线检测任务上,将DCPLD-Net与最先进的点云分割算法(即pointnet++, RandLA-Net)进行了比较。DCPLD-Net在训练/推理速度、IoU和F1分数方面优于上述方法。根据对实验数据的消融实验,扩散层对F1分数的贡献约为8%,显示了混合网络设计的优越性。该网络对旋转、严重的高斯噪声和点抖动噪声表现出稳定的性能。
Abstract:
The stable and reliable supply of electric power is strongly related to the normal social production. In recent years, power transmission lines inspection based on remote sensing methods has made great progress, especially using the UAV-borne LiDAR system. The extraction and identification of power transmission lines (i.e., conductors) from 3D point clouds are the basis of LiDAR data-based power grid risk management. However, existing rule-based/traditional machine learning extraction approaches have exposed some limitations, such as the lack of timeliness and generalization. Moreover, the potential of deep learning is seriously overlooked in RoW (Right of Way) LiDAR inspection tasks. Thus, we proposed DCPLD-Net: a diffusion coupled convolution neural network for real-time power transmission lines detection from UAV-borne LiDAR data. To implement efficient 2D convolution on 3D point clouds, we proposed a novel point cloud representation, named Cross Section View (CSV), which transforms the discrete point clouds into 3D tensors constructed by voxels with a deformed geometric shape along the flight trajectory. After the CSV feature generation, the encoded features of each voxel are treated as energy (i.e., heat) signals and diffused in space to generate diffusion feature maps. The feature of the power line points are thus enhanced through this simulated physical process (diffusion). Finally, a single-stage detector named PLDNet is proposed for the multiscale detection of conductors on the diffused CSV representations. The experimental results show that the DCPLD-Net achieves an average F1 score of 97.14 % at 8 Hz detection frequency on RoWs inspection LiDAR datasets collected by both mini-UAV LiDAR and large-scale fully autonomous UAV power lines inspection robots, and surpasses compared methods (i.e. PointNet ++, RandLA- Net) in terms of F1 scores and IoU.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1569843222001558