标题:基于PSO-BP-AdaBoost多波束海底底质分类方法-以胶州湾为例
Acoustic Seabed Classification Based on Multibeam Echosounder Backscatter Data Using the PSO-BP-AdaBoost Algorithm: A Case Study from Jiaozhou Bay, China
作者:Xue Ji, Bisheng Yang, Qiuhua Tang
来源:IEEE JOURNAL OF OCEANIC ENGINEERING
摘要:
BP神经网络是常用的一种监督分类神经网络,但传统的BP神经网络具有收敛速度慢、局部极值、难确定隐含层数和隐节点数等主要问题,影响分类精度和分类效率。Adaboost是一种性能优越的boosting算法,可以训练得到的各个弱分类器联合起来形成强分类器。本文提出一种基于PSO-BP-Adaboost算法的海底底质分类方法,利用粒子群优化算法(PSO)较强的鲁棒性和全局搜索能力等优点优化BP神经网络以获得最优初始权值和阈值,将多个优化后的BP神经网络组成Adaboost强分类器,用于解决海底底质类型多样化、类型之间差异较小等多分类难点问题。
本文构建详细的反向散射声强数据处理模型(图1)对胶州湾采集到的多波束数据进行补偿改正,生成高质量海底声呐镶嵌图(图2);
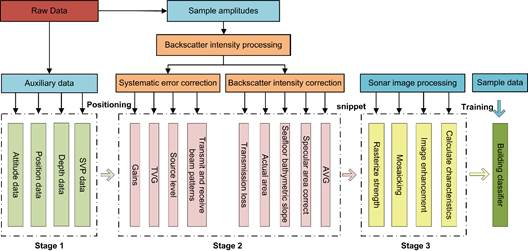
图1. 多波束反向散射声强补偿改正模型
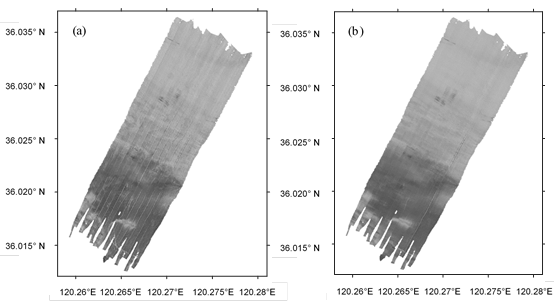
图2. (a)研究区散射强度镶嵌图,没有经过校正。(b)校正后的声强镶嵌图 (1米分辨率)。
提取海底声呐图像的多维特征信息,通过ReliefF分析从提取的34维特征信息中筛选出最具分类优势的8维特征;
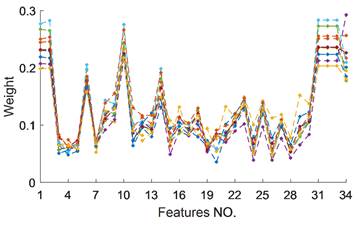
图3. 特征权值分布
对PSO-BP-Adaboost模型进行训练并测试,并与基于单层决策树的Adaboost、PSO-BP、SVM分类结果对比分析, 实验证明PSO-BP-AdaBoost分类模型具有较好的分类精度,总体精度较其他算法分别提高了12.68%、6.78%和3.56%,说明PSO-BP-AdaBoost算法可以有效地应用于声学底质分类识别,具有较高的精度。

图4. 分类结果比较
Abstract
When back-propagation neural network (BPNN) is often applied to supervised classification, problems arise, including a slow convergence rate, local extremum, and difficulty in determining the number of hidden layers and hidden nodes, that affect the classification accuracy and efficiency. These problems can be overcome by using smarter network designs. Adaptive boosting (AdaBoost) which combines multiple weak classifiers to create a strong classifier, has a strong classification advantage. In this paper, we propose an acoustic seabed classification method that combines AdaBoost with the particle swarm optimization. The PSO-BP-AdaBoost algorithm uses multibeam echosounder backscatter data to solve the multi-classification problem of diverse seafloor sediment types with small differences between types. We optimize a BPNN using the PSO algorithm to obtain the optimal initial weight and threshold and combine these to form an AdaBoost strong classifier. The input data is obtained from the sonar mosaic from multibeam echosounder backscatter data collected in Jiaozhou Bay using a series of fine processing techniques. These processing techniques result in 34-dimensional features using ReliefF analysis. The most advantageous eight-dimensional features are used as input into the AdaBoost algorithm based on one-level decision tree, PSO-BP algorithm, SVM, and PSO-BP-AdaBoost algorithm. The PSO-BP-AdaBoost classification model has better classification accuracy. The overall accuracy is improved by 12.68%, 6.78% and 3.56%, respectively, which demonstrates that the PSO-BP-AdaBoost algorithm can be effectively applied to acoustic seabed classification and identification and achieves high precision.