标题:
基于层次化匹配的消费级无人机
LiDAR
系统数据质量改善
A hierarchical approach for refining point cloud quality of a low cost UAV LiDAR system in the urban environment
来源:
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
对于消费级无人机
LiDAR
系统来说,平台中搭载的低成本
POS(position and orientation system
,定位定姿系统)误差大,导致直接地理定向点云数据质量差。对移动测量系统获取的数据进行轨迹纠正与扫描到地图匹配是两种常见的点云数据质量改善方法。而现有的轨迹纠正方法大多假设
POS
误差可以用时变函数建模,但这一假设难以用于低成本
POS
。此外,现有的扫描到地图匹配难以用于存在较大扫描间隔的无人机
LiDAR
系统中。
为了克服上述问题,本文提出
HR-ULS
,即基于层次化匹配的消费级无人机
LiDAR
系统数据质量改善方法,将原始激光数据划分为一系列扫描块,并分别在扫描块内部和扫描块间进行优化,从而实现局部和全局的点云数据一致性。运用本文提出的方法在自主研发设计的消费级无人机
LiDAR
系统珞珈麒麟云(如图1)上做了验证和测试。在三个典型城市场景中,经过
HR-ULS
处理,无人机点云平面拟合误差由
0.34 m
降低到
0.09 m
,地面检查点误差由
1.86 m
降低到
0.21 m
,达到了与高精度
POS
系统
APX-15-UAV
一致的直接地理定向结果,极大降低了轻小型无人机
LiDAR
系统对高端测绘级
POS
的依赖。
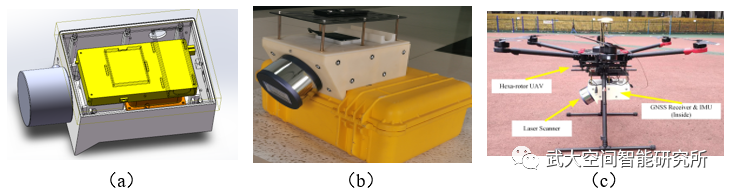
图1 消费级无人机LiDAR硬件系统设计与集成
(a) 硬件原理设计;(b) KylinCloud-II样机;(c)无人机载荷
本文技术流程如图2所示,首先提出了一种扫描块内部优化策略(
ISBM,internal scan-block matching
),采用了一种新颖的多尺度分布计算方式,将激光帧转化为点分布,从而实现了准确的帧匹配。其次,提出了一种多视扫描块优化策略(
MSBM,multiview scan-block matching
),融合了
GNSS
观测、
IMU
观测、以及激光观测,对原始无人机轨迹进行了修正,克服了现有方法对无人机轨迹进行时变函数假设的不足。

图2 消费级无人机LiDAR数据层次化匹配技术流程
实验结果
为了验证本文提出方法的有效性,利用自主研发的轻小型无人机LiDAR系统-珞珈麒麟云(KylinCloud-II)分别在三个城市环境中采集了三组实验数据及检查点,如图3所示。经过本文提出的
HR-ULS
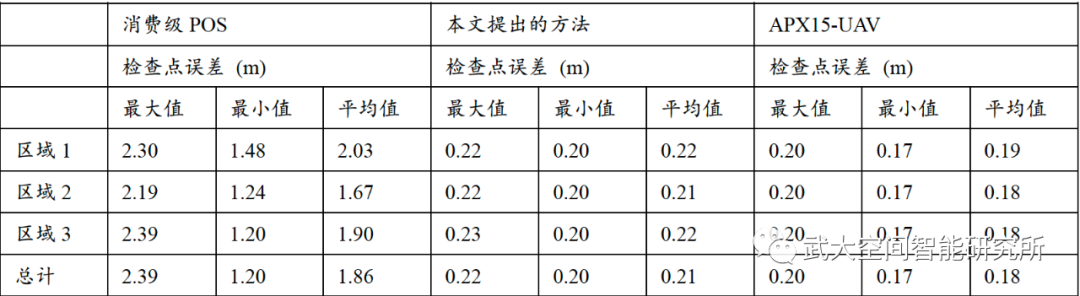
方法处理,轻小型无人机LiDAR系统数据质量有了明显的改善,如图4所示。通过分析表1中地面检查点误差分布,可以发现本文提出的方法有效降低了点云误差,可以达到与高精度POS系统APX-15-UAV一致的水平。改善前后数据对比见文末视频:HR-ULS。
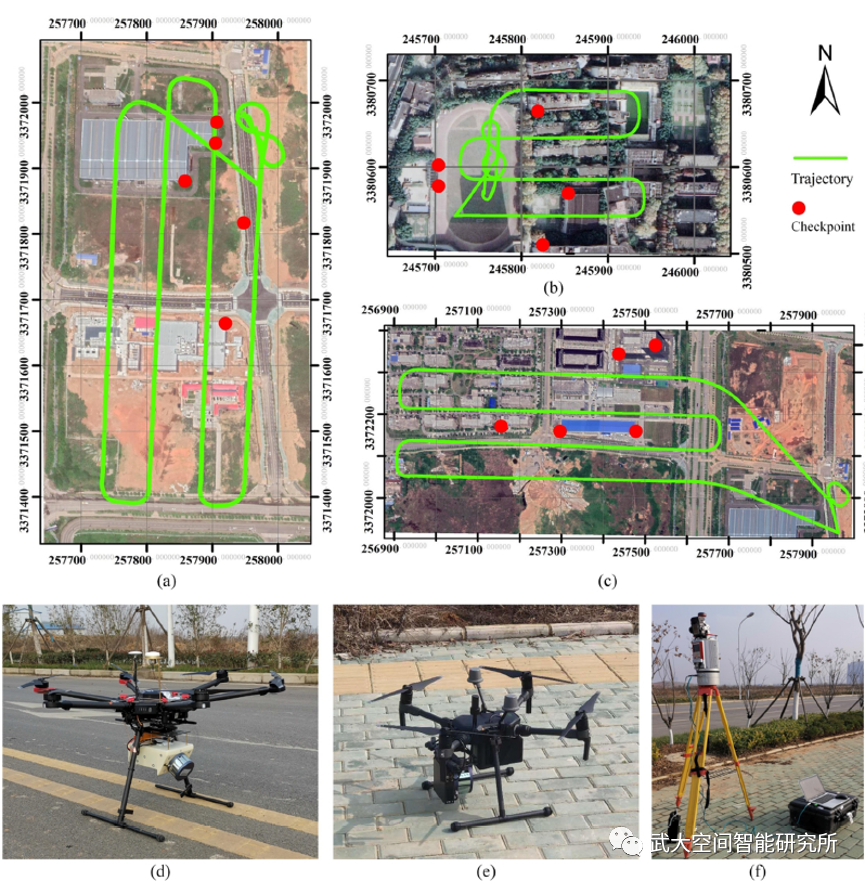
图3 实验数据采集
(a)(b)(c) 三个典型城市场景;
(d)
消费级无人机LiDAR系统;
(e) 搭载APX-15-UAV的蜂鸟无人机LiDAR系统;(f) 利用VZ-400进行地面检查点采集

图4 消费级无人机LiDAR数据改善前后对比
(a) 解算后的点云;(b) 改善前点云;(c) 改善后点云
表1 地面检查点误差分布
对比视频:HR-ULS
Abstract
Insufficient accuracies of the low end position and orientation system (POS) used in low cost UAV LiDAR systems (ULSs) cause the direct georeferencing data to lead to poor point cloud quality. Trajectory correction and scan-to-map matching are two commonly used strategies for point cloud quality refinement. The existing trajectory correction strategies work with the assumption that POS errors can be modeled as a time-variant function, which cannot be applied to the low end POS. The existing scan-to-map matching methods have difficulty refining the ULS point clouds due to the large gaps between scan lines. This paper proposes HR-ULS, hierarchical refinement for low cost ULS point cloud quality in the urban environment, to solve these challenges. HR-ULS separated the raw laser scanning point clouds into a set of scan-blocks and refined the point cloud quality with a hierarchical strategy, resulting in local and global optimization, respectively. First, the internal scan-block matching (ISBM) estimated multiscale distributions for each laser frame and calculated relative motions iteratively to achieve local map consistency in each scan-block. Second, the multiview scan-block matching (MSBM) took inertial, Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), and laser measurements into a unified adjustment framework to correct the trajectory, achieving global map consistency between scan-blocks. Comprehensive experiments evaluated the proposed HR-ULS with the point clouds captured by a low-cost ULS in three typical urban areas. They showed that the average plane fitting RMSE of the ULS point clouds was improved from 0.34 m to 0.09 m, and the average checkpoint offset was improved from 1.86 m to 0.21 m, achieving an identical level of accuracy with that of direct georeferencing using a high end POS, APX-15-UAV.