标题:基于相对定向模型的车载LiDAR点云与全景图像序列自动配准方法
Automatic Registration of Mobile Mapping System Lidar Points and Panoramic-Image Sequences by Relative Orientation Model
作者:Ningning Zhu, Bisheng Yang, Zhen Dong, Chi Chen, Xia Huang, and Wen Xiao
来源:Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing
摘要:
论文提出一种全景图像的相对定向模型(PROM),并将其应用于车载LiDAR点云与全景图像序列的配准,该模型适用于全景图像位置和姿态参数均未知情况下的配准工作。首先,使用SURF算法从相邻两幅全景图像中提取并匹配特征点;其次,将匹配的特征点带入相对定向模型解算相邻图像间的相对位置与姿态参数;然后,结合起始全景图像的绝对位姿参数,依次得到序列全景图像的绝对位姿参数,实现全景图像序列与LiDAR点云的自动配准;最后,将本文方法与手工选取同名特征点求解方法对比。实验结果表明,本文方法适用于不同场景下点云与全景图像序列的配准,该方法将点云与图像的配准转化为图像间特征点的匹配,因此相比于目前已有的配准方法具有更广泛的适用性。
技术流程:
本文的技术路线和实验数据分别如图1和图2所示。
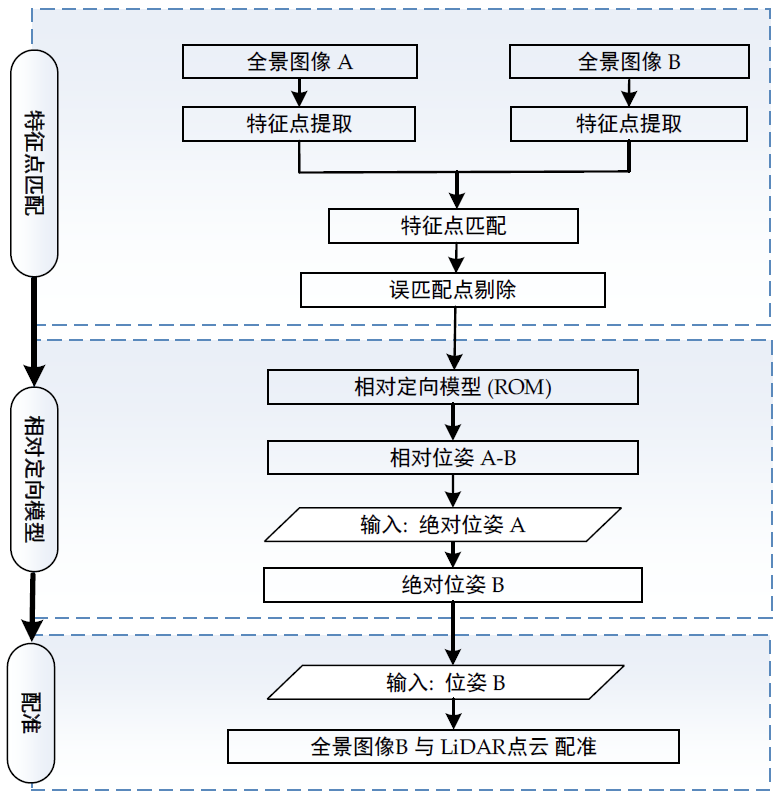
图1 技术路线

图2 实验数据,(a)LiDAR点云 (b)全景图像
对全景图像序列进行特征点匹配和误匹配点剔除,如图3所示:
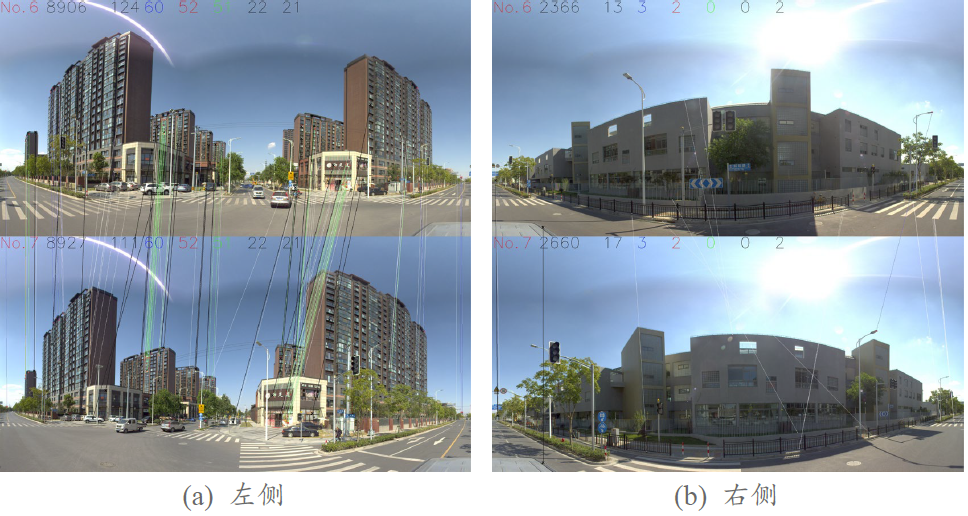

图3 特征点匹配
利用匹配的特征点解算相对位姿参数,并结合起始图像的绝对位姿参数,实现序列全景图像与LiDAR点云的配准,实验结果如图4所示:
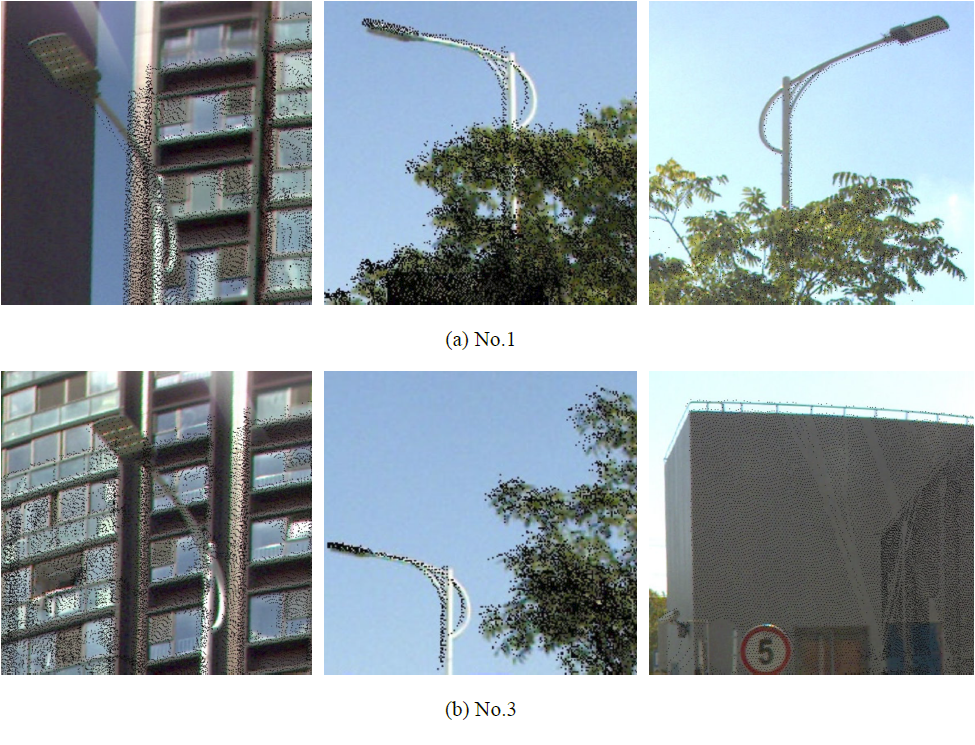

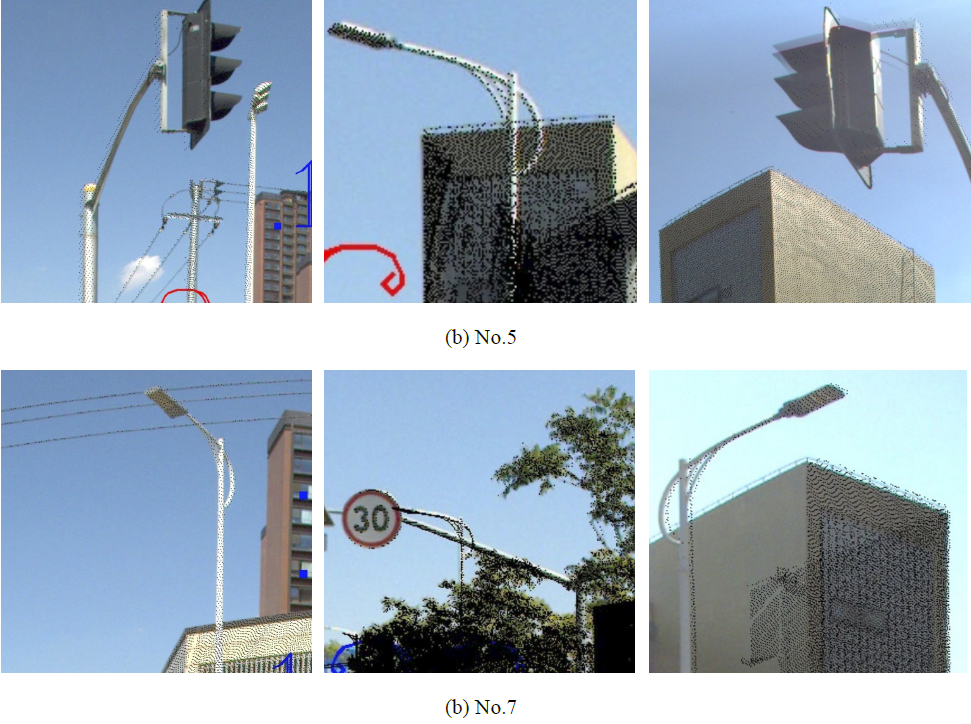
图4 全景图像1, 3, 5和7的局部配准效果
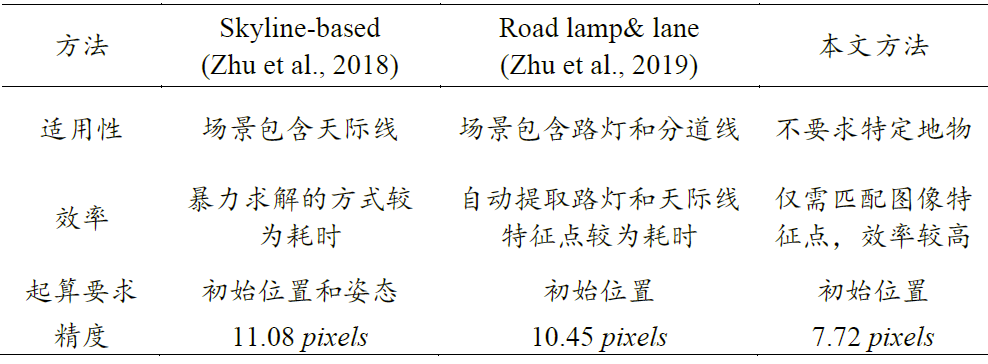
将本文方法与已有配准方法进行对比,如表1所示:
表1 不同配准方法之间的比较
结论:
论文提出使用全景图像的相对定向模型(PROM)进行车载LiDAR点云与全景图像序列的配准,并使用不同场景下的数据验证该方法的精度和适用性,跟已有方法相比,论文中方法最大的创新在于将点云与图像的配准转化为图像特征点的匹配,从而避免了从点云中进行特征提取的繁琐工作,因此本论文方法具有更大的适用范围。
致谢:
该论文得到国家杰出青年科学基金(41725005)、国家自然科学基金(42101446)、测绘遥感信息工程国家重点实验室专项科研经费和广西自然资源遥感院项目(GXZC2019-G3-000703-GXDC)资助。
Abstract
To register mobile mapping system (MMS) lidar points and panoramic-image sequences, a relative orientation model of panoramic images (PROM) is proposed. The PROM is suitable for cases in which attitude or orientation parameters are unknown in the panoramic-image sequence. First, feature points are extracted and matched from panoramic-image pairs using the SURF algorithm. Second, these matched feature points are used to solve the relative attitude parameters in the PROM. Then, combining the PROM with the absolute position and attitude parameters of the initial panoramic image, the MMS lidar points and panoramic-image sequence are registered. Finally, the registration accuracy of the PROM method is assessed using corresponding points manually selected from the MMS lidar points and panoramic-image sequence. The results show that three types of MMS data sources are registered accurately based on the proposed registration method. Our method transforms the registration of panoramic images and lidar points into image feature-point matching, which is suitable for diverse road scenes compared with existing methods.