标题
Autonomous Vehicle Localization with Prior Visual Point Cloud Map Constraints in GNSS-Challenged Environments
作者
Xiaohu Lin,Fuhong Wang,Bisheng Yang,Wanwei Zhang
来源
Remote Sensing
摘要
准确的车辆自主定位是自动驾驶汽车完成高级导航任务的关键。最先进的定位方法采用视觉和光检测和测距(LiDAR)同时定位和映射(SLAM)来估计车辆的位置。但是,由于长期运行而没有循环优化或先前的约束,它们都可能遭受错误累积。实际上,车辆不能总是返回到重新访问的位置,这将导致在全球导航卫星系统 (GNSS) 挑战环境中累积错误。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的定位方法,该方法具有由立体相机生成的先验密集视觉点云图约束。首先,采用半全局块匹配(SGBM)算法估计每一帧的视觉点云,并使用立体视觉里程计提供当前视觉点云的初始位置。其次,对先验密集视觉点云图进行多重滤波和自适应先验图分割,实现快速匹配和定位。然后,通过正态分布变换(NDT)将当前视觉点云与候选子图进行匹配。最后,匹配结果用于根据最后一帧更新姿态预测,以实现准确定位。进行了综合实验以验证所提出的方法,表明平移和旋转的均方根误差 (RMSE) 分别小于 5.59 m 和 0.08°。
Abstract
Accurate vehicle ego-localization is key for autonomous vehicles to complete high-level navigation tasks. The state-of-the-art localization methods adopt visual and light detection and ranging (LiDAR) simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) to estimate the position of the vehicle. However, both of them may suffer from error accumulation due to long-term running without loop optimization or prior constraints. Actually, the vehicle cannot always return to the revisited location, which will cause errors to accumulate in Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)-challenged environments. To solve this problem, we proposed a novel localization method with prior dense visual point cloud map constraints generated by a stereo camera. Firstly, the semi-global-block-matching (SGBM) algorithm is adopted to estimate the visual point cloud of each frame and stereo visual odometry is used to provide the initial position for the current visual point cloud. Secondly, multiple filtering and adaptive prior map segmentation are performed on the prior dense visual point cloud map for fast matching and localization. Then, the current visual point cloud is matched with the candidate sub-map by normal distribution transformation (NDT). Finally, the matching result is used to update pose prediction based on the last frame for accurate localization. Comprehensive experiments were undertaken to validate the proposed method, showing that the root mean square errors (RMSEs) of translation and rotation are less than 5.59 m and 0.08°, respectively.
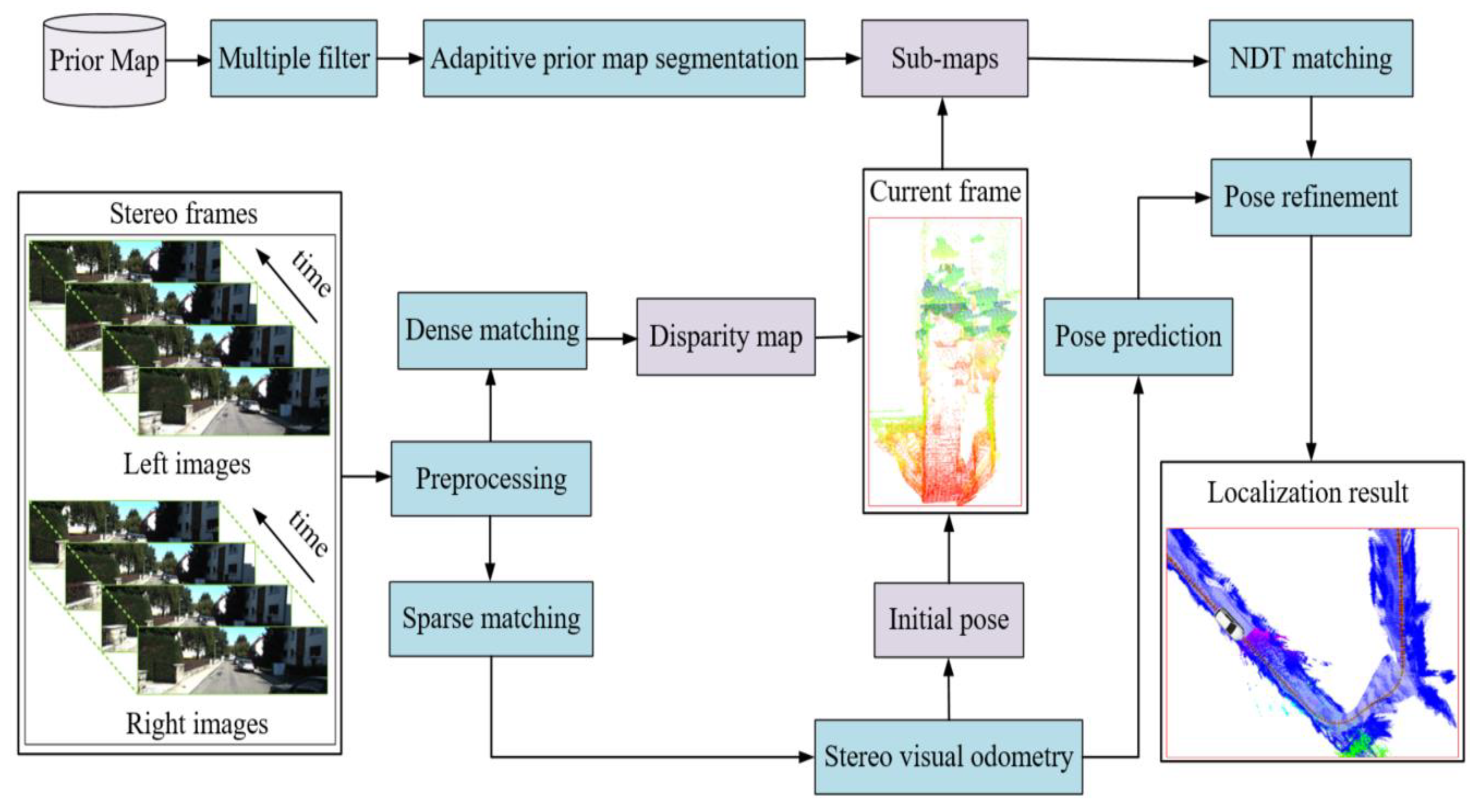
所提出的自动驾驶汽车定位流程