原文题目:CAOM:Change-aware online mapping with heterogeneous multi-beam and push-broom LiDAR point clouds
作者:丛阳滋,陈驰*,杨必胜,梁福逊,马瑞琪,张飞
来源: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing
研究动机:
在利用多线激光雷达MBL点云数据进行激光SLAM时,其误差来源主要包括两大部分,首先,由于MBL的传感器性能限制,点云观测数据自身会存在一定的测距误差,其次,点云配准作为激光SLAM核心模块之一,同样会引入精度的损失,并且这两种误差会随着激光SLAM系统的长时间运行而逐渐累积,致使点云地图精度下降。尽管通过闭环检测过程可以对此误差进行补偿,但原理上只不过是对累积误差进行重新分配,无法很好的处理由于激光测距而产生的误差。因此,联合先验点云地图的辅助定位系统成为研究的热点,借助于高精度INS系统,离线构建的点云地图通常具有较高的精度,可以为SLAM系统提供可靠的控制信息,同时也可以过滤掉场景中的运动目标,从而减少误差的累积,提升MBL三维建图的精度。另一方面,高精度的推扫式激光雷达PBL点云地图在采集过程中会存在由于视线遮挡而产生的数据缺失问题,并且数据采集成本远高于MBL,成为点云数据库的及时更新重要影响因素,而激光SLAM则可以很好地弥补上述问题,从而实现优势互补。
研究思路:
本文提出了一种融合PBL与MBL多源点云的联合优化与地图更新方法(CAOM),利用高精度的PBL点云地图纠正激光SLAM过程中的累积误差。首先利用激光里程计所估计的位姿通过可见性滤波分别提取视角追踪点云(ViTC),利用多源点云鲁棒配准模型实现高效准确的多源点云联合优化,后端采用带有控制信息的全局因子图提升激光雷达三维建图的整体精度,同时利用融合虚拟深度与距离影像的局部差异检测策略结合多视角MBL观测模型实现三维点变化概率的传播与更新,完成场景点云地图的三维变化检测,对多源点云地图数据中的差异进行有效的识别,从而实现环境三维点云地图的及时更新,方法整体流程如图1所示。
图1 融合PBL与MBL多源点云的联合优化与地图更新
实验结果:
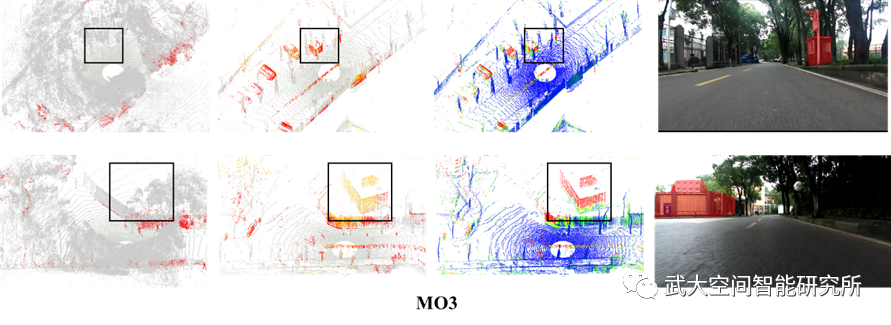
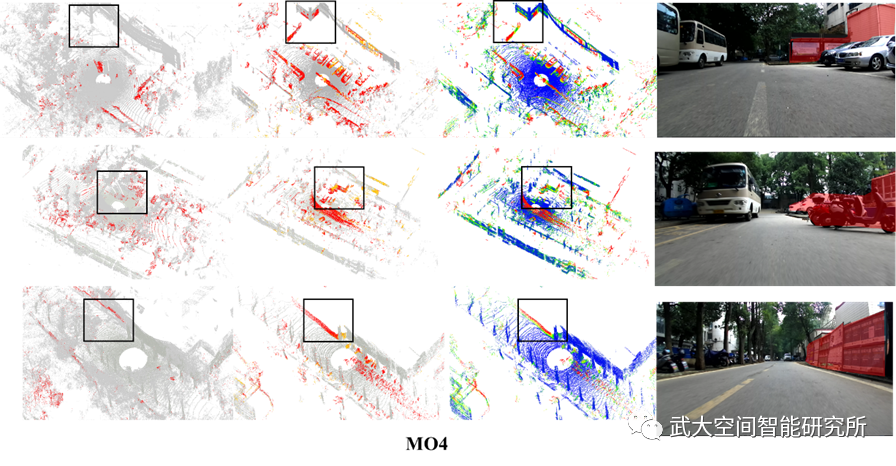

图2 局部差异检测结果。其中黑色矩形框为明显差异位置。(a)PBL局部点云地图。其中红色代表变化的点;(b)MBL局部地图单元。其中黄色表示变化的点,而红色代表新添加的三维点;(c)MBL局部地图单元。其中颜色代表距离值大小;(d)真实场景图片。红色区域为明显变化位置
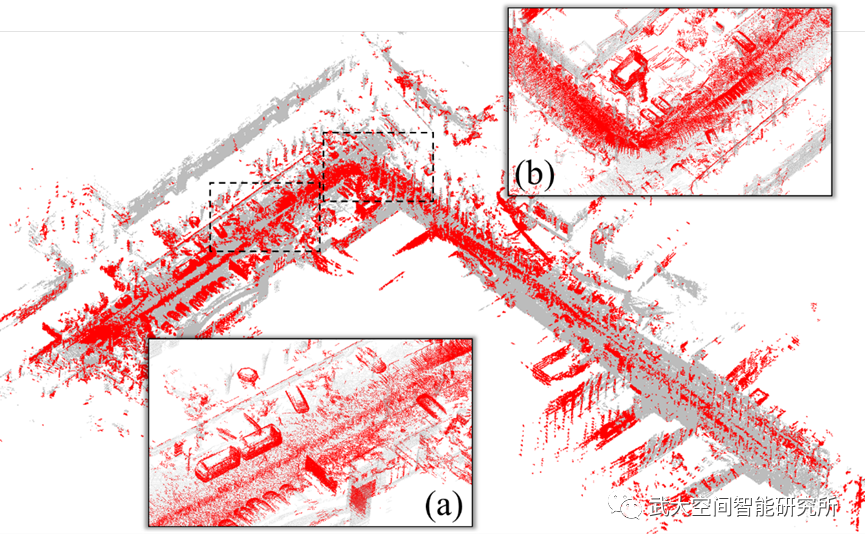
(a)MBL地图中检测的差异
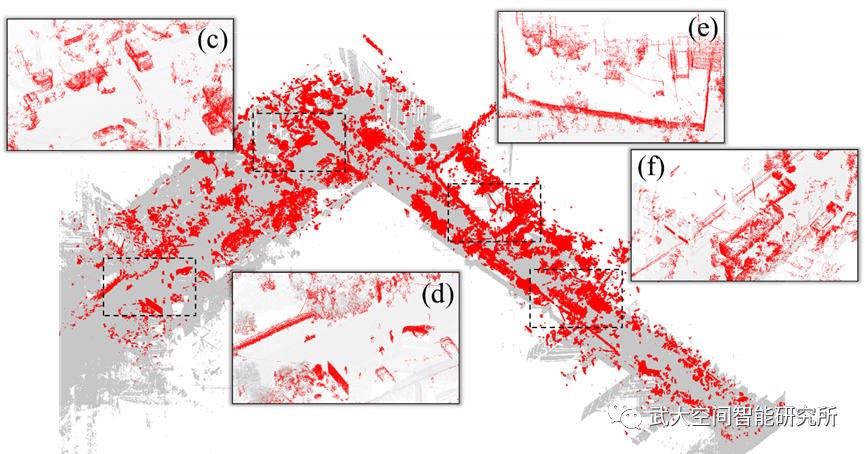
(b)PBL地图中检测的差异
图3 MO4数据点云地图中的差异
Abstract:
A High-Definition (HD) map is an essential component not only for autonomous vehicles but also for surveyors in favor of city management. Moreover, the HD map must be up-to-date by reflecting environmental changes continuously. The development of LiDAR Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) techniques has provided an effective way to collect precise point clouds for the construction of HD maps, while traditional methods are time-consuming and labor-intensive on account of the complex street scene. Furthermore, life-long 3D mapping is quite necessary and challenging nowadays. In this paper, we introduce a novel change-aware 3D online mapping framework CAOM, using point clouds collected by Multi-Beam LiDAR (MBL) and Push-Broom LiDAR (PBL) for rapid city map update and change detection. Concerning the prior map with higher precision, heterogenous fusion is performed to rectify the SLAM drift, based on the View-Traced Clouds (ViTC) derived according to their view in common. Meanwhile, corresponding virtual range images are integrated with distance images to detect the 3D changes between the current map and the historical reference map offline. The detection results are later fused in a probabilistic way along with the homogeneous fusion process where a resilient graph consisting of diverse factors is established to maintain the local and global consistency of the final point cloud map. Compared with 3D-CSTM, the real-world experiments have shown an average 0.5 m and max 1.5 m improvement in the ATE (Absolute Translation Error) of the trajectory generated by our system. Quantitative measurements on the individual point accuracy are also conducted to verify the performance of 3D mapping with up to 16% improvement in comparison with respect to the 3D-CSTM method. The effects of the disparity detection and probabilistic fusion can be revealed from the small objects distinguished in the point cloud map as well as > 95% overall accuracy.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0924271622003100